Design Graph With Shortest Path Calculator
Problem Statement
Leetcode: Design Graph With Shortest Path Calculator
There is a directed weighted graph that consists of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The edges of the graph are initially represented by the given array edges where edges[i] = [from_i, to_i, edgeCost_i] meaning that there is an edge from from_i to to_i with the cost edgeCosti.
Implement the Graph class:
Graph(int n, int[][] edges)initializes the object withnnodes and the given edges.addEdge(int[] edge)adds an edge to the list of edges whereedge = [from, to, edgeCost]. It is guaranteed that there is no edge between the two nodes before adding this one.int shortestPath(int node1, int node2)returns the minimum cost of a path fromnode1tonode2. If no path exists, return -1. The cost of a path is the sum of the costs of the edges in the path.
Example 1:
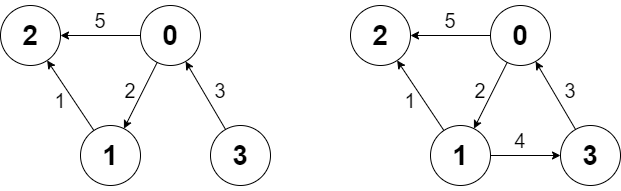
Input
["Graph", "shortestPath", "shortestPath", "addEdge", "shortestPath"]
[[4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]], [3, 2], [0, 3], [[1, 3, 4]], [0, 3]]
Output
[null, 6, -1, null, 6]
Explanation
Graph g = new Graph(4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]);
g.shortestPath(3, 2); // return 6. The shortest path from 3 to 2 in the first diagram above is 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 with a total cost of 3 + 2 + 1 = 6.
g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return -1. There is no path from 0 to 3.
g.addEdge([1, 3, 4]); // We add an edge from node 1 to node 3, and we get the second diagram above.
g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return 6. The shortest path from 0 to 3 now is 0 -> 1 -> 3 with a total cost of 2 + 4 = 6.
Solution
typedef priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> distance_queue;
class Graph {
public:
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> all_edges;
Graph(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
all_edges = vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>(n);
for(auto &edge: edges) {
addEdge(edge);
}
}
void addEdge(vector<int> edge) {
all_edges[edge[0]].push_back({edge[1], edge[2]});
}
void visitNode(int node, int baseCost, distance_queue& queue) {
for(auto &e: all_edges[node]) {
int distance = baseCost + e.second;
queue.push({distance, e.first});
}
}
int shortestPath(int node1, int node2) {
if (node1 == node2) return 0;
vector<bool> visited(all_edges.size(), false);
int minDistance = INT_MAX;
bool pathExists = false;
distance_queue queue;
visitNode(node1, 0, queue);
visited[node1] = true;
while(!queue.empty()) {
auto current = queue.top();
queue.pop();
int node = current.second;
int distance = current.first;
if (node == node2) {
minDistance = min(distance, minDistance);
pathExists = true;
} else if (!visited[node]) {
visitNode(node, distance, queue);
visited[node] = true;
}
}
return pathExists ? minDistance : -1;
}
};
/**
* Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Graph* obj = new Graph(n, edges);
* obj->addEdge(edge);
* int param_2 = obj->shortestPath(node1,node2);
*/
